
When evaluating stocks, we try to look for companies protected by a moat. In this context, a “moat” is an advantage that some businesses enjoy, whereby the barriers to entry make it exceptionally difficult for competitors to come in, take away market share and undercut prices.
Airports are one such business model that can be characterized this way.
Think about it: With few exceptions, most cities and metropolitan areas around the world can support only one airport. When you fly commercially, you generally do not have a choice as to which hub you arrive at. Take our hometown of San Antonio, Texas, as an example. Despite it being home to more than 1.5 million people, the city has only one international airport.
From an investment point of view, we believe this monopolistic market power makes airports particularly attractive.
American readers will no doubt find that last statement odd. Here in the U.S., we tend to think of airports more as public utilities than businesses. That’s because today there are no publicly traded airports in the United States. Again, to use San Antonio as an example, the city’s international airport is owned and operated by the city itself.
Elsewhere, it’s a different story. There are about 15 publicly traded airport stocks available around the world, mostly in Latin America, Western Europe, East Asia and Oceania. Some of the more well-known examples include Beijing Capital International Airport Co. Ltd.; Aeroports de Paris SA, which operates Paris’ three main commercial airports; and Grupo Aeroportuario del Sureste S.A.B. de C.V., which operates as many as nine airports in Mexico’s southeastern states. Most of them are available to U.S. investors through American depositary receipts (ADRs).
Attractive Margins
We like airports not just because they’re about as close to monopolies as you can get. They can also be highly profitable businesses, despite having huge fixed costs—not unlike airlines.
Airports have two types of revenue streams: aeronautical and non-aeronautical. Aeronautical includes revenue generated from the carriers that use their services. Think fees associated with landing, parking, transfers and the like. In 2017, such fees accounted for about 56% of airports’ income, according to Airports Council International (ACI).
The other revenue stream, non-aeronautical, is derived mostly from passengers and includes retail concessions, duty-free, car parking, food and beverage, advertising, rental car concessions and more.
If you’ve spent any time in an airport, you know there’s a million and one ways to spend money while waiting for your connecting flight.
Before the pandemic, airports were becoming havens for high-end shopping, generating a growing share of global sales for luxury goods companies. Over the years, they’ve learned to capitalize on captive flyers, many of them high-net worth individuals, who have time between flights to browse in Louis Vuitton and Chanel. For every dollar they spend, the airport receives a cut.
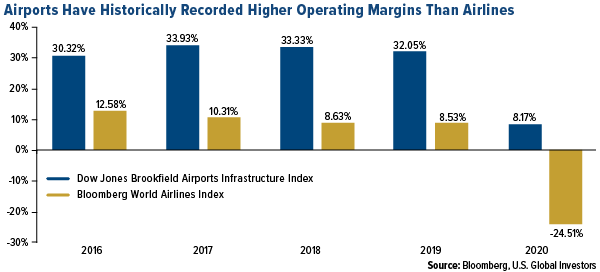
This has helped listed airports record extremely attractive operating margins in recent years. In the four years before the pandemic, they’ve had an average margin of around 32%, roughly three times greater than global airlines’ average margin. In 2020, airports’ operating margin remained positive at 8.17%, while airlines saw theirs fall to -24.51%.
Rotating into Airports
Earlier we mentioned that listed airports are available to U.S.-based investors through ADPs. That’s true, but there’s also another way: the U.S. Global Jets ETF (JETS).
As the name implies, JETS invests in the global airline industry. That includes not just carriers but also aircraft manufacturers and airports. The ETF rebalances and reconstitutes on a quarterly basis.
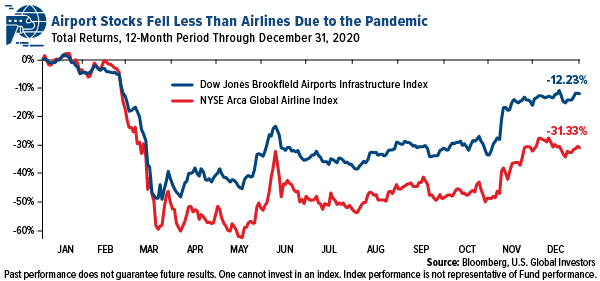
At the last rebalance, we kicked out the laggards, most of them pandemic-impacted airlines, and rotated into airports, which have held up slightly better than carriers. The Dow Jones Brookfield Airports Infrastructure Index, which has only 12 constituents, ended 2020 down 12.23%, while the NYSE Arca Global Airline Index fell 31.33%, or about 2.5 times more.
As of January 13, JETS held as many as 11 airport or airport services stocks.
We believe that this is a prudent allocation as the pandemic continues to rage and affect scheduled flights.
Unlike many industry-specific ETFs, JETS is based on so much more than just market cap. It’s a dynamic, smart-beta 2.0 ETF, meaning it uses a multi-factor methodology to screen for companies with the strongest fundamentals.
Check with your brokerage firm today to make sure it’s carrying JETS! In the meantime, explore the ETF’s top holdings by clicking here.
The Dow Jones Brookfield Airports Infrastructure Index is a global index that is designed to measure the performance of pure-play infrastructure companies in the airports sector. The NYSE Arca Global Airline Index is a modified equal- dollar weighted index designed to measure the performance of highly capitalized and liquid international airline companies. The Index tracks the price performance of selected local market stocks or ADRs of major U.S. and overseas airlines. The Bloomberg World Airlines Index is a capitalization-weighted index of the leading airlines stocks in the World.
Operating margin measures how much profit a company makes on a dollar of sales after paying for variable costs of production, such as wages and raw materials, but before paying interest or tax. It is calculated by dividing a company’s operating income by its net sales. An American depositary receipt (ADR) is a negotiable certificate issued by a U.S. depository bank representing a specified number of shares of a foreign company’s stock. The ADR trades on U.S. stock markets as any domestic shares would.
Smart beta defines a set of investment strategies that emphasize the use of alternative index construction rules to traditional market capitalization-based indices. Smart betaemphasizes capturing investment factors or market inefficiencies in a rules-based and transparent way.
All opinions expressed and data provided are subject to change without notice. Some of these opinions may not be appropriate to every investor.
The outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic and the resulting actions to control or slow the spread has had a significant detrimental effect on the global and domestic economies, financial markets and industries, including airlines. U.S. Global Investors continues to monitor the impact of COVID-19, but it is too early to determine the full impact this virus may have on commercial aviation. Should this emerging macro-economic risk continue for an extended period, there could be an adverse material financial impact to the U.S. Global Jets ETF.
